Understanding the main symptoms of these diseases helps to get proper treatment and to avoid timely complications, so we have described in detail the differences in this article.
Contribution of an accurate diagnosis is possible after the study:
- General analysis of blood and urine,
- a biochemical blood test,
- Samples and X -s
- MRI and examination of synovial fluid - if necessary.
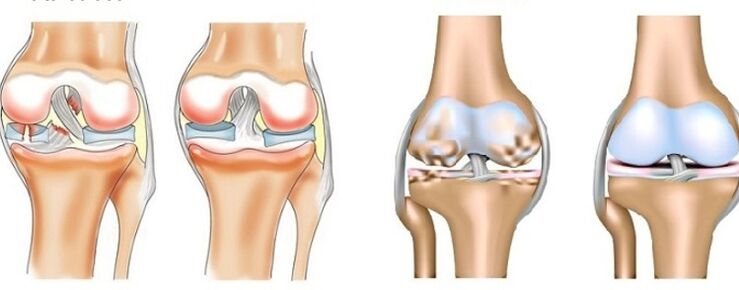
Arthritis
Arthritis is a disease that provokes infection, failure in the functioning of the immune system or metabolism. The main sign of arthritis is the inflammatory process: swelling, redness of the skin and fever in the area of the affected joint. The negative effect of arthritis can be expanded not only to the joints: the heart, kidneys and liver are in the risk zone. There are more than two hundred types of arthritis with different manifestations and causes in the risk zone people of young and middle age. 18% of the disability falls on arthritis according to WHO statistics
Symptoms
The first signs of the disease are generally:
- Acute pain - in a state of movement or rest,
- edema in the area of the diseased joint - permanent or periodically arising,
- Redness and elevated temperature of the affected area - you can feel a touch,
- The restriction of movements in the morning.
Arthritis can occur in a hidden form - in this case the symptoms occur after exposure to provocative factors: stress, fatigue, hypothermia or infection.
Symptoms also include manifestations of the inflammatory process in the body:
- fever up to 38-39 degrees;
- loss of strength and chills;
- conjunctivitis;
- Change in blood test indicators: for example, an increase in ESR and a high level of white blood bodies;
- Pain during urination.
The severity of manifestation of arthritis may be different and progress is not necessarily fast. However, if you do not pay attention to the problem, arthritis infuses in chronic form and can lead to disruption of the work of internal organs and damage: inability, change of joints and limbs.
Treatment and prevention
The prescribed treatment will depend on the severity of the diagnosis. If the patient has not found damage to the internal organs during the diagnosis, treatment is relatively simple. The patient can be prescribed:
- anti -inflammatory and analgesic drugs,
- physiotherapy procedures,
- adherence to diet and rejection of alcohol,
- Reducing physical activity on the affected joint.
In the case where the disease has been affected by the organs, the patient is subjected to additional primary treatment programs aimed at supporting:
- Additional exams,
- Medical therapy,
- Special diet.
Among the various forms of arthritis are some serious diseases that are important for diagnosis over time:
- Rheumatism is an inflammatory disease of the connective tissue that affects large and medium joints, and also has specific manifestations: it can dramatically manifest itself and go to different joints, as if moving from one to another.
Rheumatism does not deform the joints, but lack of treatment is fraught with serious complications: for example, kidney disease and heart defect.
The cause of the onset may be transferred infectious diseases: tonsillitis, otitis and the like. Children between the ages of 7 to 14 are most often in the risk group. Heredity also affects the development of the disease.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disease in which the inflammatory process affects both joints and many organs. For example, eyes, light, heart and blood vessels. It belongs to the group of systemic connective tissue diseases. Most often, women after 60 years suffer from the disease.
It progresses slowly, affects several joints at a time and spreads symmetrically. With the development of the disease, joints lose mobility, pain and swelling. Characteristic nodes appear on the joints affected by inflammation.
A characteristic of the diagnosis of rheumatoid is the use of special laboratory tests that allow you to establish an accurate diagnosis. Rheumatoid arthritis is treated using powerful medicines. Therefore, it is very important to suspect and diagnose this disease in the early stages.
- Gotric arthritis or gout is a progressive disease of the joints, which occurs due to impaired uric acid metabolism in the blood and the deposits of salts in the joint tissues. Most often it starts with the lesion of the thumbs.
Usually, elderly people, mainly men, suffer from gout. But there are also cases of disease in the young age.
Treatment of rheumatism, systemic diseases, gout differs from treatment, for example, allergic or reactive arthritis. Only a doctor can prescribe the correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
The disease is easier to prevent than to treat, so we recommend that you take care of prevention and carefully monitor your health:
- abandonment of bad habits - smoking, drinking alcohol, irrational nutrition;
- To develop a habit of rational sports game - loading, stretching, balanced training;
- Strengthening the immune system Consult doctor with respect to mineral-vitamin complexes, flu vaccinations.
For arthrosis
70% of cases of disease fall on people over 65 years.
Arthrosis is a disease that leads to deformity and destruction of the joint capsule. The article surface is a cartilage that covers the surface of the joint and does not allow the bones to come in contact with each other: it provides free and painless movement. Most often, arthrosis develops in the elderly. It is also called "Pianists' disease and athletes" who often suffer from arthrosis due to constant strain on the wrists and joints of the legs: thigh, knee, ankle. Arthrosis, unlike arthritis, only affects the joints and is not inflammatory.
Symptoms
Symptoms of arthrosis occur gradually as the disease progresses. At the beginning of development, they are not at all. This is the main reason to see a doctor in the late stages.
The first symptoms of arthrosis show themselves:
- joint occurs after a sleep or a long break that quickly passes during movement;
- crispy, grinding and clicks, which are accompanied by dull sound;
- Pain during movement and load.
In the short stages of arthrosis, the symptoms become more noticeable: the immobility of the joints and the pain syndrome increases, the "hard joint" syndrome develops and -the replacement of the soft cartilage tissue with the growth of the bones. The development of the chronic form of the disease leads to the inability to move one or more joints.
Treatment and prevention
Arthrosis is better treated in the early stages of the disease. Also, the chances of recovery depend on age - up to 40 years of age to get rid of the disease are much easier. Under these conditions, the patient prescribes loads on the inflamed joint, drug and shock wave therapy with theft on the bones and connective tissues with acoustic impulses with a significant low frequency amplitude: from 16 to 25 Hz. Other procedures may be used: for example, mud applications, electrophoresis with drugs. The chronic form of the disease, as well as the elderly arthrosis, does not undergo treatment. However, competent and regular therapy helps to control the disease as much as possible: to stop the destruction of the joint and improve the quality of the patient.
During such therapy, the doctor prescribes treatment with drugs that activates the regeneration process and also makes recommendations for lifestyle.
Primary prevention helps prevent the development of arthrosis. Basic principles:
- Weight control - excess weight increases joint load;
- Regular physical activity - gymnastics, stretching and moderate training;
- Choosing high quality and comfortable shoes - the wrong load distribution causes increased pressure on the joints;
- Strengthening immunity and protection against hypothermia.
Visual comparison
We have described the main causes, symptoms and methods for treating arthritis and arthrosis. In this block, we briefly answer the question of the difference in disease:
| Arthritis | Arthrosis |
| An inflammatory disease that affects the joints and can affect the normal functioning of the internal organs. | The disease is degenerative, destructive, character. It only affects the joints of the joints. |
| It develops mainly in people of young and middle age: 25-45 years. This also happens in children. | In principle, it is ahead of the elderly, as well as the people whose activities are directly related to the load of the joints: athletes, musicians, artists. |
| It is manifested by inflammatory symptoms at the initial stage: pain, redness and fever in the affected area. | It may not be a long time, slow progress - this complicates the diagnostic process at an early stage. |
Be healthy!























